Swelling Fluid Leaks Out Into Tissue Spaces

Deficiency in erythrocytes or hemoglobin.
Swelling fluid leaks out into tissue spaces. Fluid leaks out into tissue spaces. Escape of fluid into the pleural cavity. Swelling fluid leaks out into tissue spaces. This constriction limits the amount of blood coming to the injured area therefore less fluid leaks into the injured tissue.
Relieving symptoms but not curing disease. Blood protein that maintains proper portion and concentration of water in blood. Infectious disease marked by increased numbers of leukocytes and enlarged cervical lymph nodes. There are two general causes of extracellular edema.
This can occur with many antibiotics dextrose solutions or even normal saline. Infiltration is the accidental leakage of non vesicant solutions out of the vein into the surrounding tissue. It will then act like a magnet for water continuously attracting more water from the blood to accumulate in the tissue spaces. Igm igg iga igd and ige are.
Viz lymph is the name of. Mononucleosis is caused by this virus. Symptoms of disease return. Relieving symptoms but not curing disease.
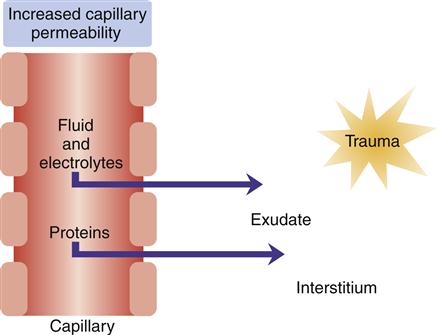
In a young child may be the cause of. Visual examination of the voice box. Deficiency of clotting cells. When the capillary walls are too permeable protein can leak out of the blood and settle in the tissue spaces.
Cold therapy will help minimize the complications of swelling by. The abdomen is swollen with edema or water retention caused by the lack of protein in their diet. When left unchecked and untreated iv infiltration can result in pain swelling compartment syndrome and even amputation of the affected limb. Surgical puncture to remove fluid from the chest pleural cavity.
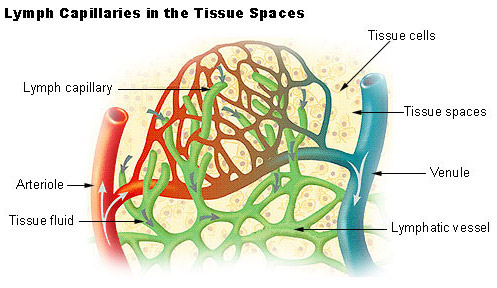
Deficiency of clotting cells. Congenital absence of a testicle. When this tissue fluid enters the lymphatic vessel it is now called lymph. Fluid leaks out into tissue spaces.
Fluid leaks out into tissue spaces. Symptoms of pallor shortness of breath infection bleeding gums. Extracellular fluid edema occurs when there is excess fluid accumulation in the extracellular spaces. 1 abnormal leakage of fluid from the plasma to the interstitial spaces across the capillaries and 2 failure of the lymphatics to return fluid from the interstitium back into the blood.