Submandibular Space

The submandibular space is a suprahyoid deep compartment of the head and neck.
Submandibular space. The submandibular nodes are small usually measuring approximately 1 centimeter in a healthy adult. The submandibular space extends from the hyoid bone to the mucosa of the floor of the mouth and is bound anteriorly and laterally by the mandible and inferiorly by the superficial layer of the deep cervical fascia. Submandibular space infection is acute cellulitis of the soft tissues below the mouth. Terminology within this compartment all authors include the space within the submandibular triangle around the submandibular gland.
As the sublingual space is not bounded by fascia posteriorly some authors consider the sublingual space a component of the submandibular space 2. Water covered a large space at the end of the valley. More commonly however the sublingual and submandibular spaces are discussed separately 3 5. Gross anatomy the sublingual space is a part of the floor of mouth 1.
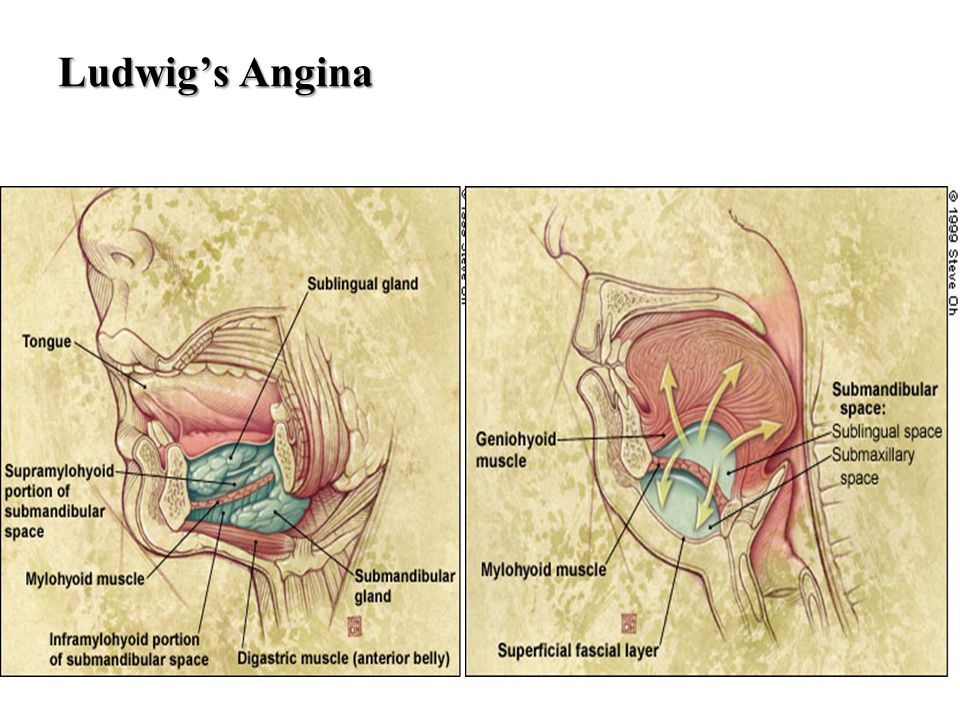
The submandibular space is a fascial space of the head and neck. Ludwig s angina is a bilateral infection of the submandibular space that consists of two compartments in the floor of the mouth the sublingual space and the submylohyoid also known as submaxillary space. It is a potential space and is paired on either side located on the superficial surface of the mylohyoid muscle between the anterior and posterior bellies of the digastric muscle. It was first described by the german physician wilhelm frederick von ludwig in 1836.
People with poor dental hygiene and people who have had a tooth pulled or a jaw fracture are at higher risk. The mylohyoid muscle separates it superiorly from the sublingual space which communicates with it freely around the posterior border of the mylohyoid. A submandibular space infection is a bacterial infection of the floor of the mouth. The submaxillary space is a historical term for the combination of the submandibular submental and sublingual spaces which in modern practice are referred to separately or collectively termed the perimandibular spaces.
Symptoms include pain dysphagia and potentially fatal airway obstruction. The submandibular duct which brings lymph fluid to the node is approximately 5 to 6 centimeters. Diagnosis usually is clinical. Bacteria can spread from an infected lower tooth to the tissue under and around the tongue.