Dilated Perivascular Space
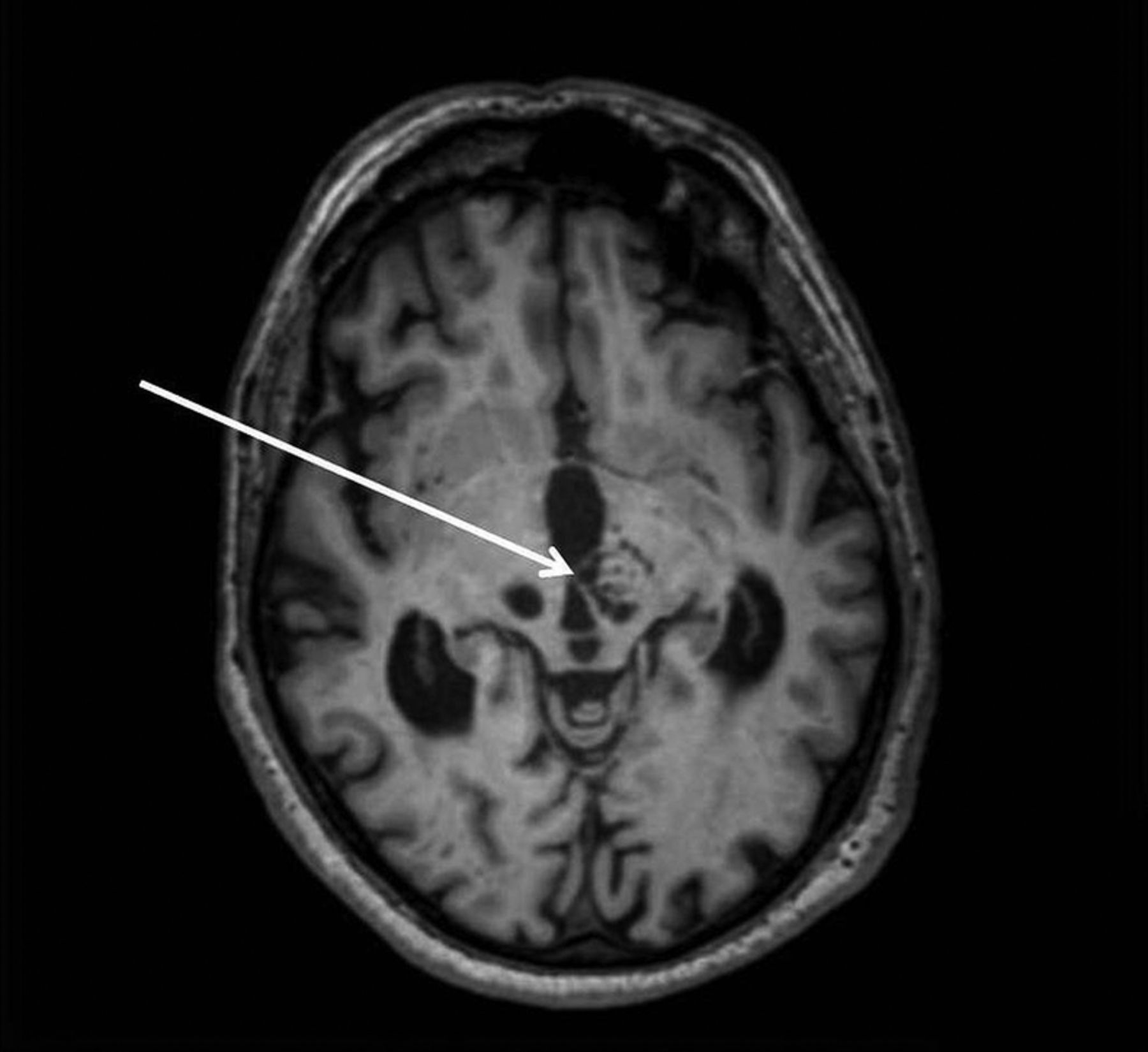
Our aim was to examine the discriminative power of dilated cerebral perivascular spaces as biomarkers of small vessel disease in a very elderly population of patients with dementia.
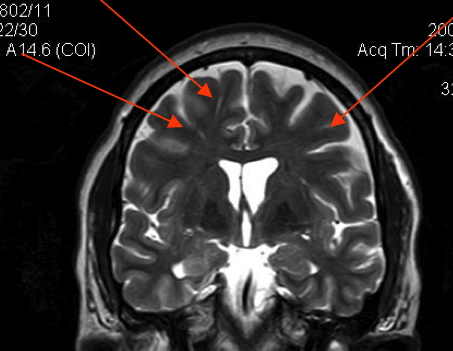
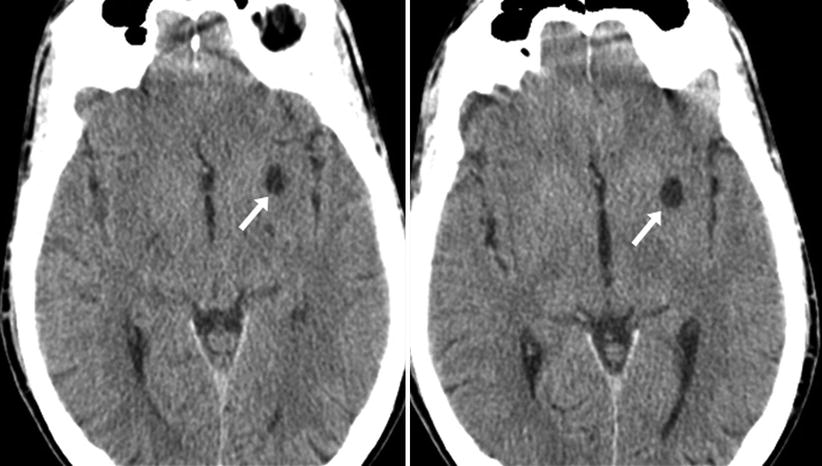
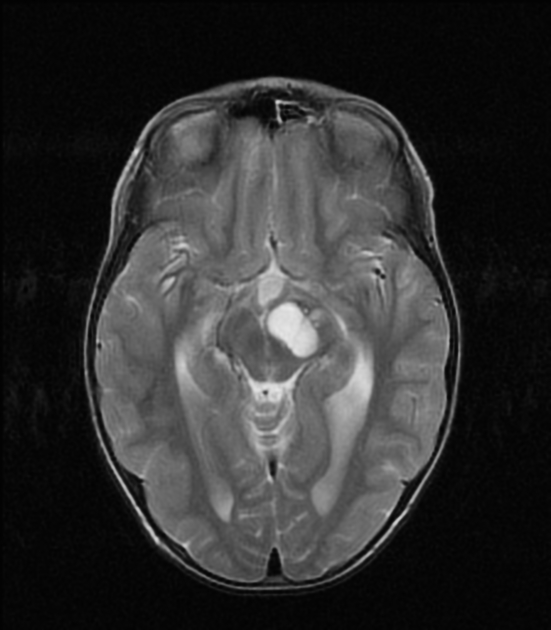
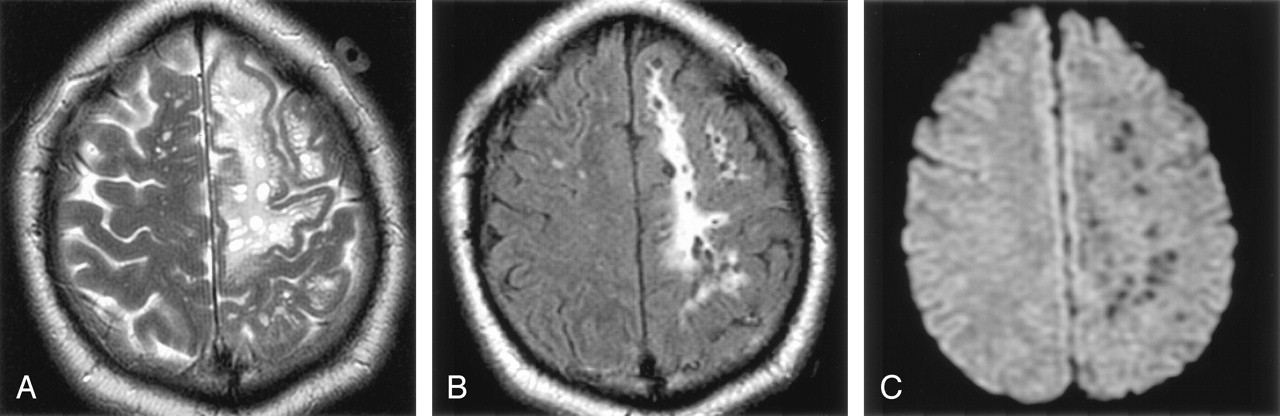
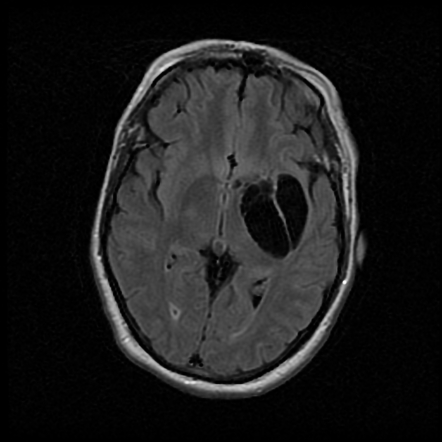
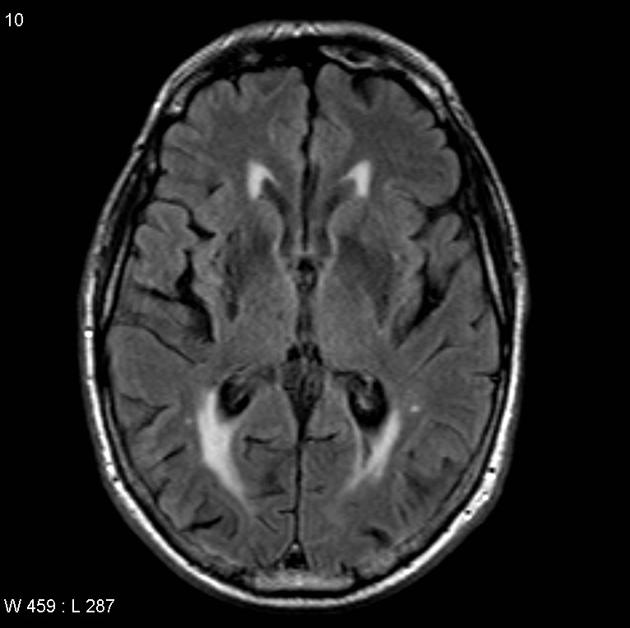
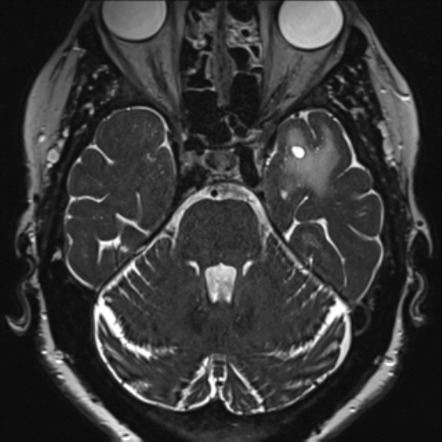
Dilated perivascular space. Perivascular spaces which are visible on imaging are typically less than 5 mm in diameter but can reach much larger sizes. A perivascular space also known as a virchow robin space is a fluid filled space surrounding certain blood vessels in several organs including the brain potentially having an immunological function but more broadly a dispersive role for neural and blood derived messengers. Recent animal and human studies have shown an increased frequency of enlarged high convexity virchow robin spaces vrs in several neurologic diseases suggesting their role as neuroradiologic markers of inflammatory changes. They tend to enlarge with age and hypertension.
Dilated perivascular spaces consist of regular cavities containing an artery. Dilated vrs could provide a passive access to cns of blood borne cells which in turn could trigger or enhance the inflammatory process. A so called giant perivascular space or tumefactive perivascular space and can exert enough mass effect to be symptomatic 1. Dilated perivascular spaces have been shown to be a specific biomarker of cerebral small vessel disease in young patients with dementia.
Enlarged perivascular spaces epvs or virchow robin spaces are cerebrospinal fluid filled cavities that surround small penetrating cerebral arterioles and correspond with extensions of the subarachnoid space. It is considered to be dilated when the size exceeds 2 mm visualized better in t2 weighted images. We believe that the enlargement of the perivascular space might reflect the accumulation of inflammatory cells and or changes of vascular permeability. The brain pia mater is reflected from the surface of the brain onto the surface of blood vessels in the subarachnoid space.
Dilated perivascular spaces are principally places where the axons and the myelin sheath used to be. With the 1 5 t scanners concentrations of pathology as small as 2mm could be seen. The mechanism that occurs is not well known but there are many hypotheses in study. The myelin sheath is the insulation like substance that protects most axons in the brain.
In the brain perivascular cuffs are regions of leukocyte aggregation in the perivascular.